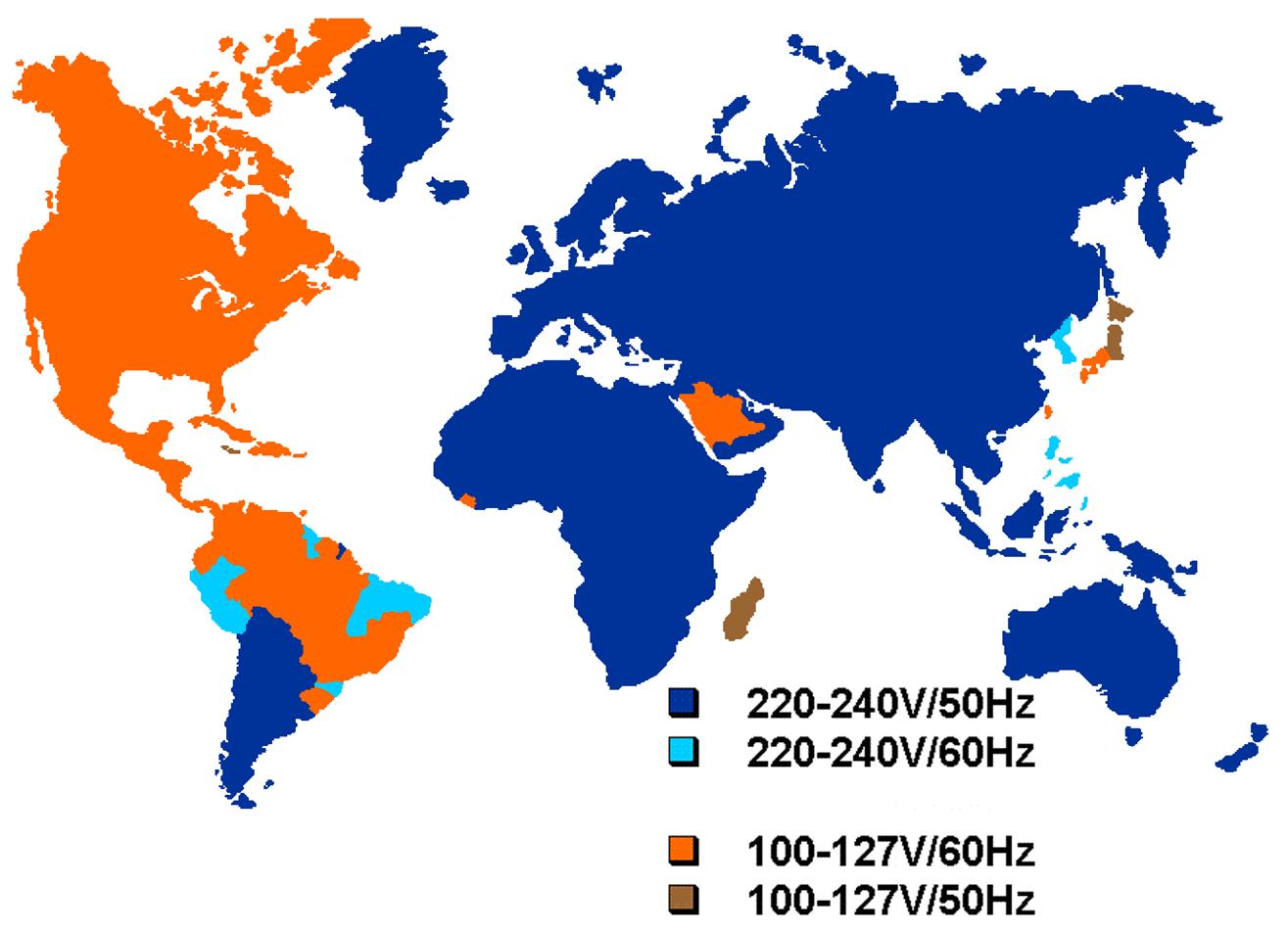
The standard outlet voltage used in homes and buildings varies by country. Understanding these differences is important for homeowners, engineers, manufacturers, and anyone using electrical equipment internationally. The most common systems are 110–120 volts and 220–240 volts, each developed based on historical and technical factors.
Standard Home Outlet Voltage Explained
The standard home outlet voltage refers to the nominal voltage supplied to residential wall sockets. In many countries, including China, most of Europe, and large parts of Asia, the standard home outlet voltage is 220V to 240V at 50Hz. This higher voltage allows electrical appliances to operate efficiently with lower current.
In contrast, some countries use lower residential voltages, most notably the United States and Canada, where the standard home outlet voltage is approximately 120V at 60Hz. Despite the difference, both systems are considered safe when installed according to modern electrical standards.
The table below shows the standard outlet voltage, frequency, and plug type used in some of the most popular countries and regions worldwide. This information is useful for understanding international power standards and ensuring electrical equipment compatibility.
| Country / Region | Standard Home Outlet Voltage | Frequency | Common Plug Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 120V | 60Hz | Type A / B |
| Canada | 120V | 60Hz | Type A / B |
| China | 220V | 50Hz | Type A / C / I |
| United Kingdom | 230V | 50Hz | Type G |
| Germany | 230V | 50Hz | Type C / F |
| France | 230V | 50Hz | Type C / E |
| Australia | 230V | 50Hz | Type I |
| Japan | 100V | 50Hz / 60Hz | Type A |
| India | 230V | 50Hz | Type C / D / M |
| Singapore | 230V | 50Hz | Type G |
| United Arab Emirates | 230V | 50Hz | Type G |
| Brazil | 127V / 220V | 60Hz | Type C / N |
American Voltage Standard
The American voltage standard is based on a nominal supply of 120 volts for most household outlets, with a frequency of 60Hz. This standard originated from early electrical system designs and remains in use today.
In the United States, higher-power appliances such as electric ovens, dryers, and HVAC systems often use 240V split-phase power, which is derived from two 120V lines. This approach allows both standard and high-power devices to operate efficiently within the same electrical infrastructure.
Why Do Outlet Voltage Standards Differ?
Differences in the standard outlet voltage are largely the result of historical decisions made during early electrification. Once power grids, wiring, and appliances were established, changing voltage standards became impractical due to cost and safety concerns.
Today, most countries maintain their original voltage systems, while modern electrical equipment is increasingly designed to support wide voltage input ranges, such as 100–240V, to ensure global compatibility.
Impact on Electrical Equipment
Voltage differences affect how electrical devices are designed and used. Equipment that is not rated for the local standard home outlet voltage may require a voltage converter or transformer. Industrial equipment, UPS systems, and power supplies are often available in region-specific voltage versions to match local grid standards.
Conclusion
The standard outlet voltage and standard home outlet voltage differ across countries due to historical and technical reasons. The American voltage standard uses 120V at 60Hz, while many other regions use 220–240V at 50Hz. Understanding these standards helps ensure safe and efficient operation of electrical equipment worldwide.