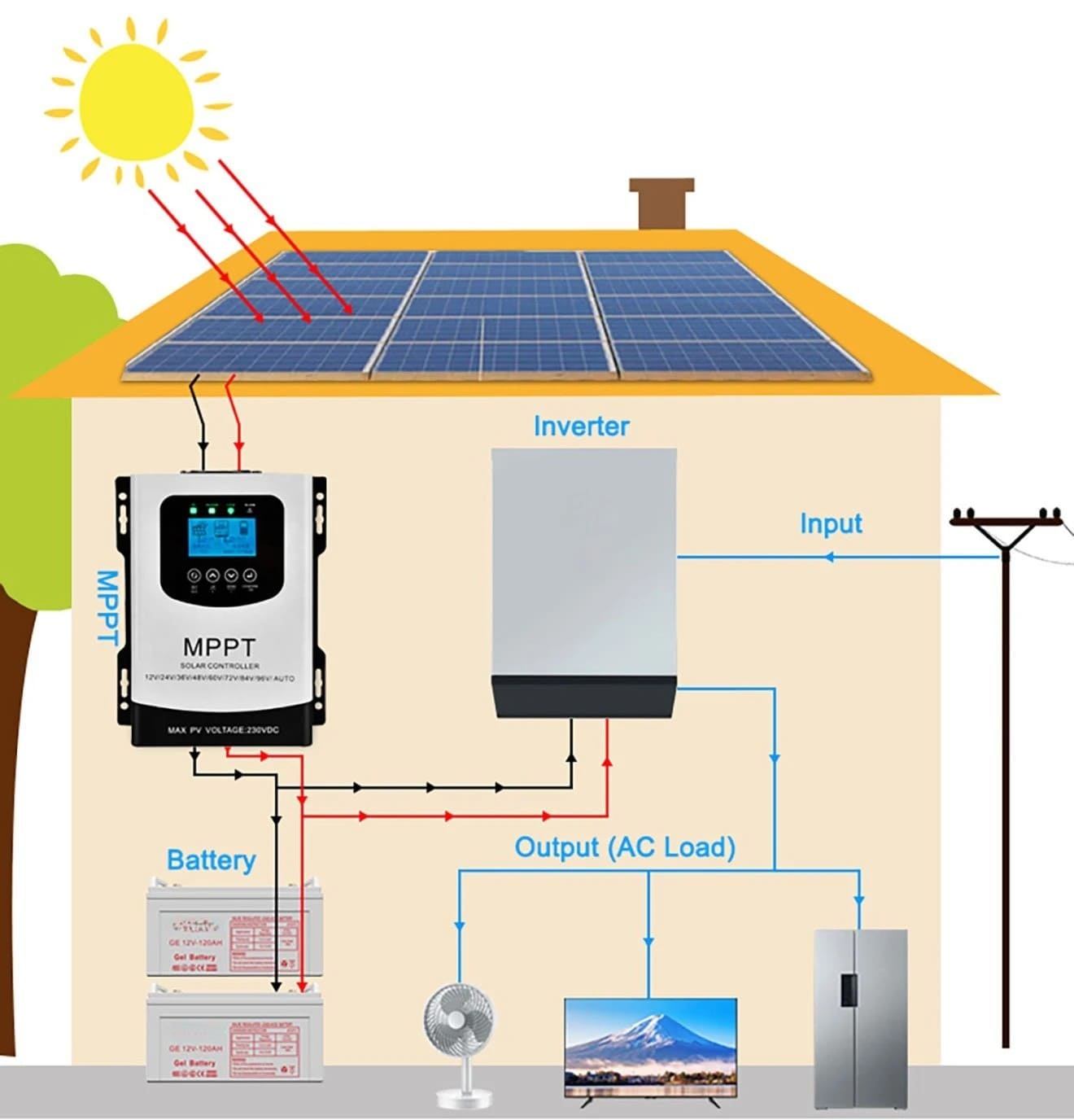
MPPT Solar Charge Controller: Maximizing Battery Charging Efficiency
Everything you need to know about MPPT solar charge controllers—how they work, why they’re more efficient than PWM, how to size and wire them, and how to protect your solar battery investment.
What is an MPPT Solar Charge Controller?
An MPPT solar charge controller (Maximum Power Point Tracking) optimizes the voltage and current from your solar panels so your battery bank receives the highest possible charging power. Unlike PWM controllers that simply match panel voltage to battery voltage, MPPT units convert excess voltage into extra charging current, boosting harvest and improving battery health.
Key Benefits
- Higher efficiency: Converts excess PV voltage into usable charging current.
- Better in low light: Tracks the maximum power point as conditions change.
- Flexible arrays: Use higher-voltage strings to reduce wire losses.
- Battery protection: Multi-stage charging improves lifespan.
Common Use Cases
- Off-grid cabins & tiny homes, off-grid battery banks
- RVs, vans, and marine systems
- Hybrid storage for residential/commercial
- Telecom/remote monitoring sites
How MPPT Charge Controller Solar Technology Works
Each solar array has a sweet spot—its Maximum Power Point—where voltage × current is highest. Temperature, irradiance, and shading constantly shift this point. An MPPT solar battery charge controller uses a tracking algorithm to continuously adjust the array’s operating voltage toward that point, then performs DC-DC conversion so the battery receives optimal charging current.
Tip: Cold panels have higher voltage. MPPT takes advantage of this by converting that extra voltage into additional charging amperage.
MPPT vs PWM: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | MPPT | PWM |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High; tracks MPP and converts voltage to current | Lower; panel voltage pulled toward battery voltage |
| Best For | Mixed weather, long wire runs, higher-V arrays | Small, budget builds with short runs |
| Array Voltage | Can exceed battery voltage significantly | Should closely match battery voltage |
| Low-Light Performance | Better tracking and harvest | More loss under variable conditions |
| Cost | Higher upfront | Lower upfront |
How to Size an MPPT Solar Charge Controller
- Choose battery bank voltage (e.g., 12V / 24V / 48V).
- Estimate charge current:
Array Watts ÷ Battery Voltage. - Add 25–30% headroom for safety and conditions.
- Verify PV input voltage stays below controller’s max rating.
- Ensure Vmp falls within MPPT tracking range.
- Check short-circuit current rating and wiring safety.
Must-Have Features in an MPPT Solar Battery Charge Controller
- Wide PV input range
- Programmable multi-stage charging
- Remote monitoring options and backup integration (mini DC UPS systems)
- Temperature compensation
- Comprehensive safety protections
- High efficiency (≥96%)
Summary
The MPPT solar charge controller is the heart of a high-performing solar power system. By tracking the maximum power point and converting excess voltage into usable charging current, an MPPT solar battery charge controller ensures faster, smarter charging and longer battery life—especially under changing weather conditions and with higher-voltage arrays.