In modern power-critical environments, efficiency has become a defining performance indicator for an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Beyond simply providing backup power, a UPS must operate with high electrical efficiency to reduce energy losses, control operating costs, and support sustainability goals. This article explores UPS efficiency in detail, explaining what it means, how it is measured, and why it matters for different applications.
What Is UPS Efficiency?
UPS efficiency refers to the ratio of usable output power delivered to connected loads versus the input power drawn from the utility source. It is typically expressed as a percentage:
UPS Efficiency = (Output Power ÷ Input Power) × 100%
An efficient UPS converts electrical power with minimal losses during rectification, inversion, filtering, and battery charging. Power losses mainly occur in the form of heat, which directly impacts energy consumption, cooling requirements, and component lifespan.
Why Efficiency Matters in Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems
UPS efficiency has a direct influence on both operational and financial performance. In data centers, industrial plants, hospitals, and telecom facilities, UPS systems operate continuously, often at partial load. Even small efficiency improvements can translate into significant long-term savings.
- Lower energy costs: High-efficiency UPS systems reduce electricity consumption.
- Reduced cooling demand: Less heat loss lowers air conditioning requirements.
- Improved reliability: Reduced thermal stress extends component life.
- Environmental benefits: Lower carbon footprint and improved sustainability metrics.
Efficiency by UPS Topology
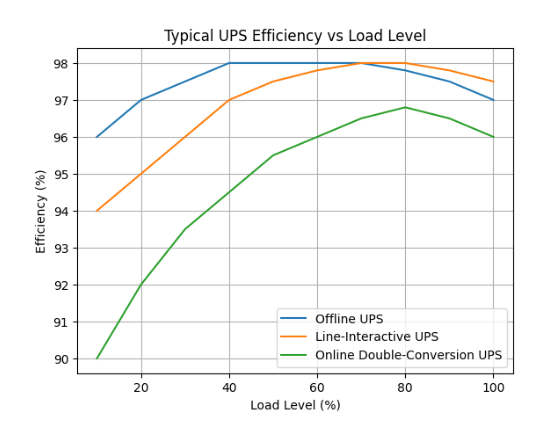
Figure: Typical UPS Efficiency vs Load Level
The chart illustrates that UPS efficiency is highly dependent on load conditions. Offline and line-interactive UPS systems maintain high efficiency under normal operation, while modern online double-conversion UPS systems achieve peak efficiency between 40% and 80% load. Proper UPS sizing is essential to avoid efficiency loss caused by prolonged low-load operation.
Online UPS has lower effiency as it takes the AC power from the wall, converts it to DC (battery power), and then converts it back to AC for your equipment. This continuous conversion process generates heat and consumes extra energy, but you got zero transfer time and perfect, clean power 100% of the time.
Offline (Standby) UPS
Offline UPS systems offer high efficiency under normal conditions because power flows directly from the utility to the load. However, protection is limited, and efficiency drops during battery operation. These systems are typically used for small office or residential applications.
Line-Interactive UPS
Line-interactive UPS designs provide voltage regulation while maintaining relatively high efficiency. They are commonly used in small server rooms and network environments where moderate protection and good energy performance are required.
Online Double-Conversion UPS
Online UPS systems deliver the highest level of power protection by continuously converting AC to DC and back to AC. Historically, this topology had lower efficiency due to double-conversion losses. However, modern designs using advanced IGBT rectifiers and inverters now achieve efficiency levels above 95%, even in double-conversion mode.
ECO Mode and High-Efficiency Operation
Many modern uninterruptible power supply systems feature an ECO mode, allowing the UPS to bypass the inverter during stable utility conditions. This can raise efficiency to 98–99% while maintaining acceptable power quality. When power anomalies occur, the UPS automatically switches back to double-conversion operation.
ECO mode is particularly beneficial in environments where energy efficiency is prioritized, though it must be carefully configured to balance efficiency and protection.
Load Level and UPS Efficiency
UPS efficiency varies depending on load conditions. Most UPS systems achieve peak efficiency between 40% and 80% load. Operating a UPS significantly below its rated capacity can reduce efficiency and increase cost per kilowatt.
Proper UPS sizing is therefore critical. Modular UPS systems offer an advantage by allowing capacity to scale with demand, maintaining high efficiency across varying load levels.
Input Power Quality and Efficiency
Efficiency is also influenced by input power characteristics. Advanced UPS systems with low input THDi and high power factor (PF ≥ 0.99) minimize harmonic distortion and reduce upstream power losses. This not only improves overall system efficiency but also protects generators and transformers.
Efficiency Standards and Certifications
UPS efficiency is often evaluated using standardized testing methods such as:
- Energy Star certification
- IEC 62040 efficiency classifications
- EU Ecodesign (ErP) requirements
These standards provide transparent benchmarks for comparing UPS performance and selecting energy-efficient solutions.
Balancing Efficiency and Reliability
While efficiency is critical, it should never come at the expense of reliability. High-efficiency UPS systems must still deliver stable voltage, clean waveforms, and fast response times during power disturbances. Modern UPS designs successfully balance both requirements through intelligent control algorithms and high-performance power electronics.
Conclusion
The efficiency of an uninterruptible power supply is a key factor in modern power protection strategy. Advancements in UPS technology have made it possible to achieve high efficiency without compromising protection, even in online double-conversion systems. By selecting the right UPS topology, operating mode, and capacity, organizations can significantly reduce operating costs, improve sustainability, and maintain reliable power for critical loads.